Our ingredients aren’t random, they’re deeply studied.
Our products are informed by high-quality, peer-reviewed clinical research, giving you confidence that they are developed with a strong scientific foundation.
PMID: 38448452
Supports a Healthy Gut Microbiome
Modern diets, stress, and antibiotic use disrupt the gut microbiome — the foundation of mental and physical health. Quercetin, along with other plant-based polyphenols, have been shown to promote microbial balance and gut resilience.
PMID: 35333451 | PMID: 34321362 | PMID: 34616111
Boost Cognitive Function
Quercetin and its microbial metabolites can cross the blood–brain barrier, helping protect neurons and support cognitive performance.
PMID: 26328470 | PMID: 17951477 | PMID: 19402938
Improve Blood Flow
Quercetin supports vascular health by enhancing nitric oxide production — helping blood vessels stay flexible and relaxed. It also helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in vessel walls, promoting smoother circulation and cardiovascular function.
The Science
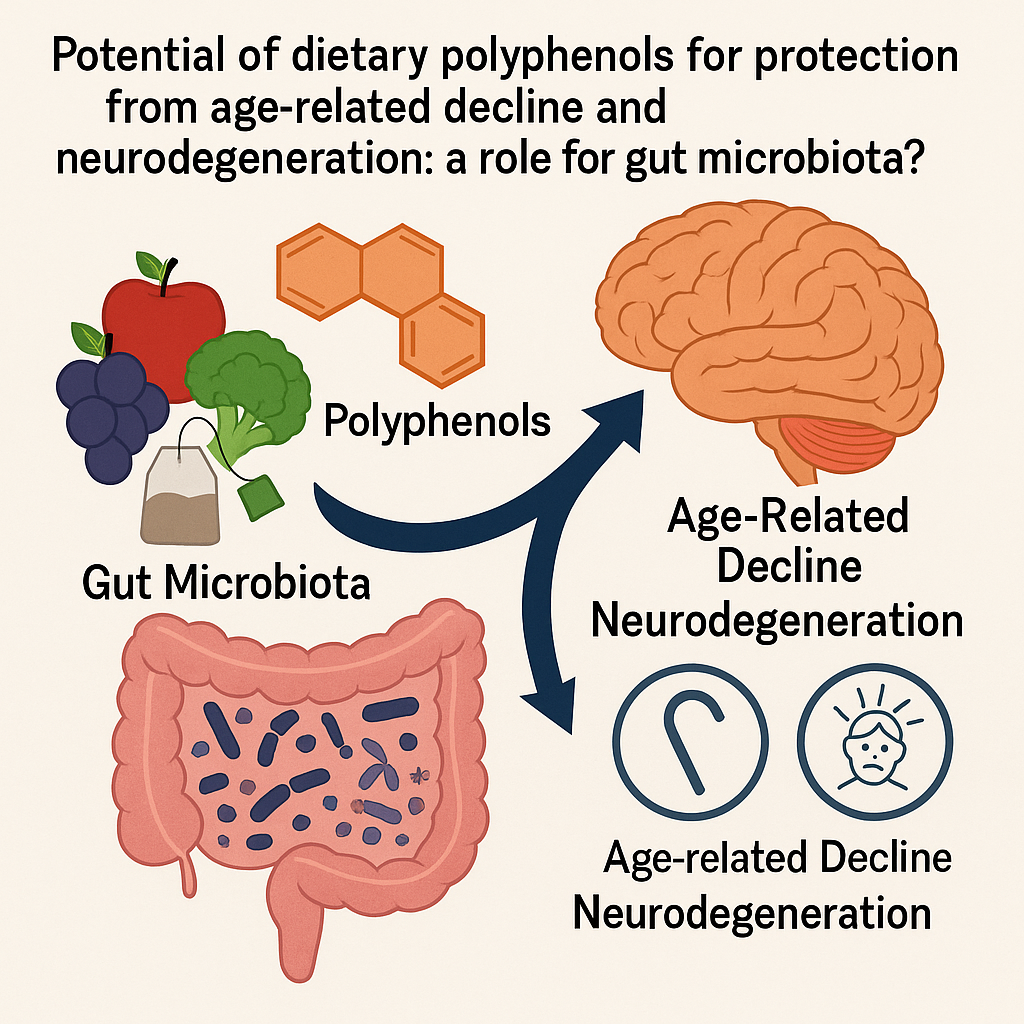
Ross et. al 2024 | PMID: 38287652
This review found that polyphenols, found in foods like fruits, vegetables, tea, and wine, may support heart and metabolic health, calm inflammation, and help regulate blood sugar. They also interact with the gut microbiome to produce beneficial compounds and may play a role in protecting brain function as we age.
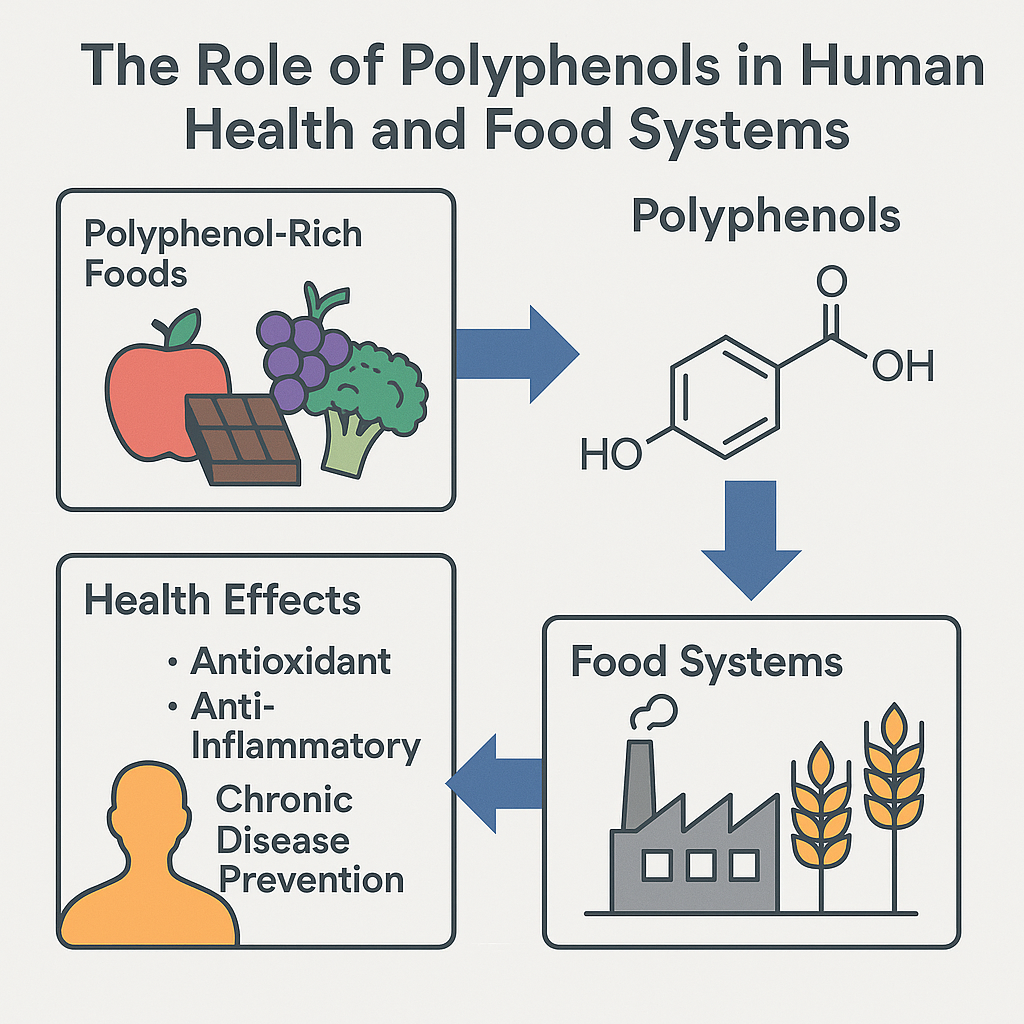
Cory et. al 2018 | PMID: 30298133
This review found that polyphenols, common in fruits, vegetables, tea, and wine, are linked to better heart and metabolic health. They may improve blood vessel function, support blood sugar regulation, and help reduce inflammation. Many polyphenols also interact with the gut microbiome, producing beneficial compounds that could contribute to healthy aging and brain protection.
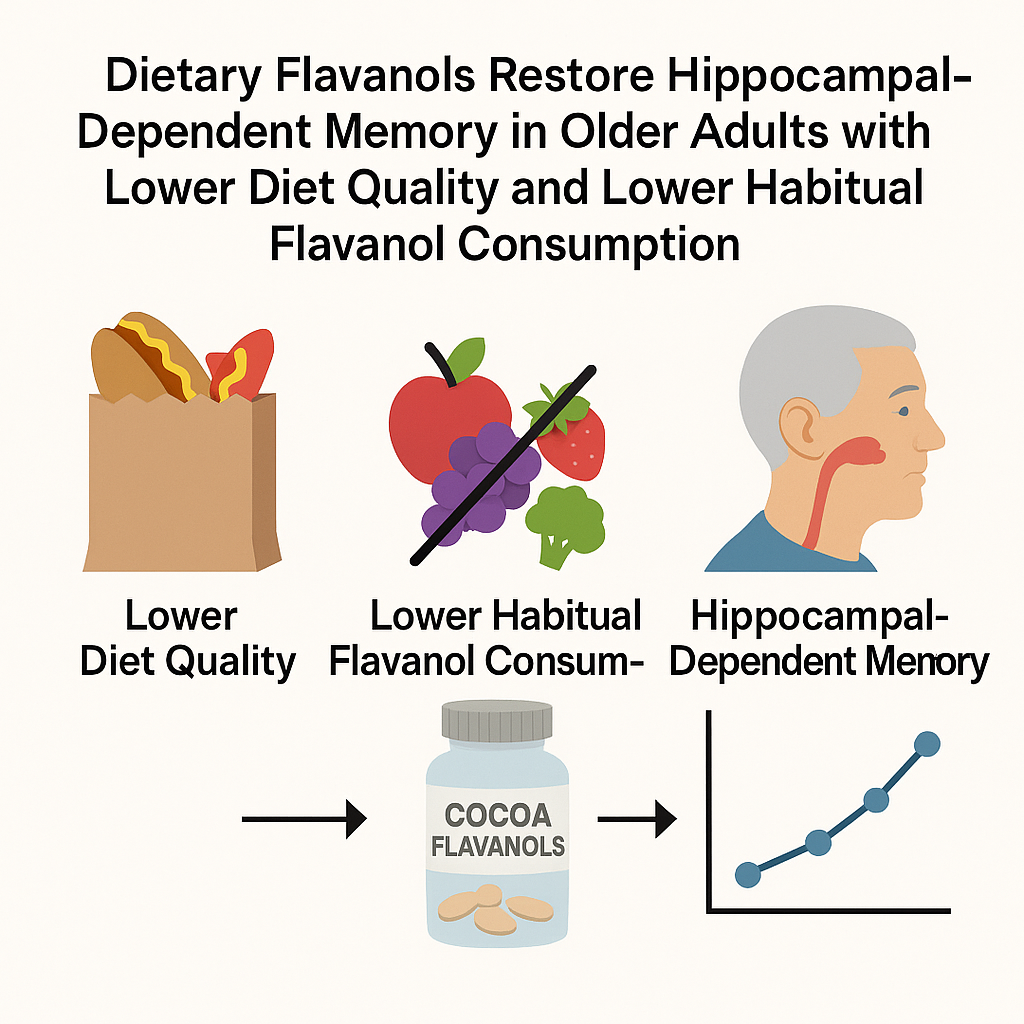
Brickman et al. 2023 | PMID: 37252983
This randomized trial found that daily supplementation with cocoa flavanols helped restore memory related to the hippocampus in older adults who initially followed a poorer diet or had low flavanol intake. Overall improvements were most significant in those with low baseline flavanol levels, suggesting that replenishing this nutrient may help support memory in later life.
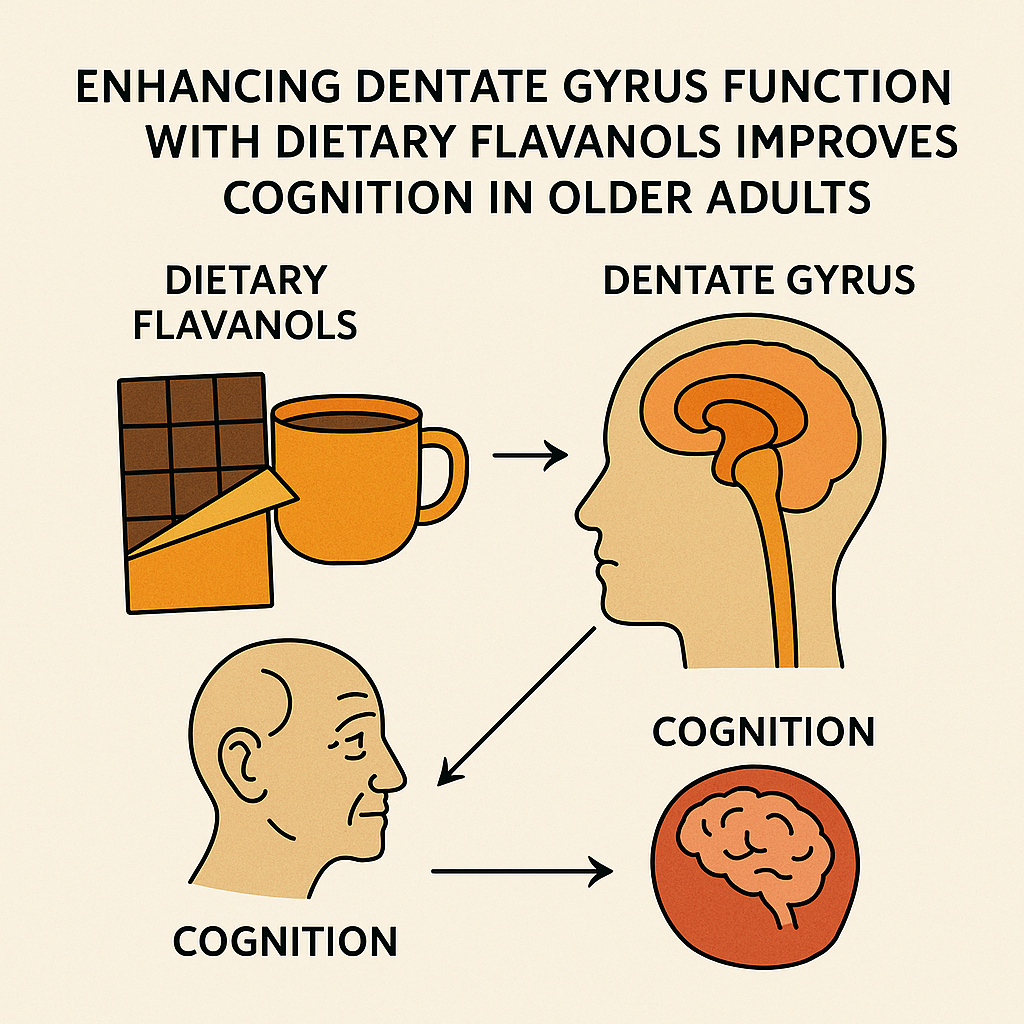
Brickman et al. 2014 | PMID: 25344629
This randomized study found that older adults who consumed a high-flavanol diet (from cocoa) for three months showed improved function in a specific brain region (the dentate gyrus), as measured by both brain imaging and memory testing. These findings suggest that increasing flavanol intake may help counteract age-related memory decline.
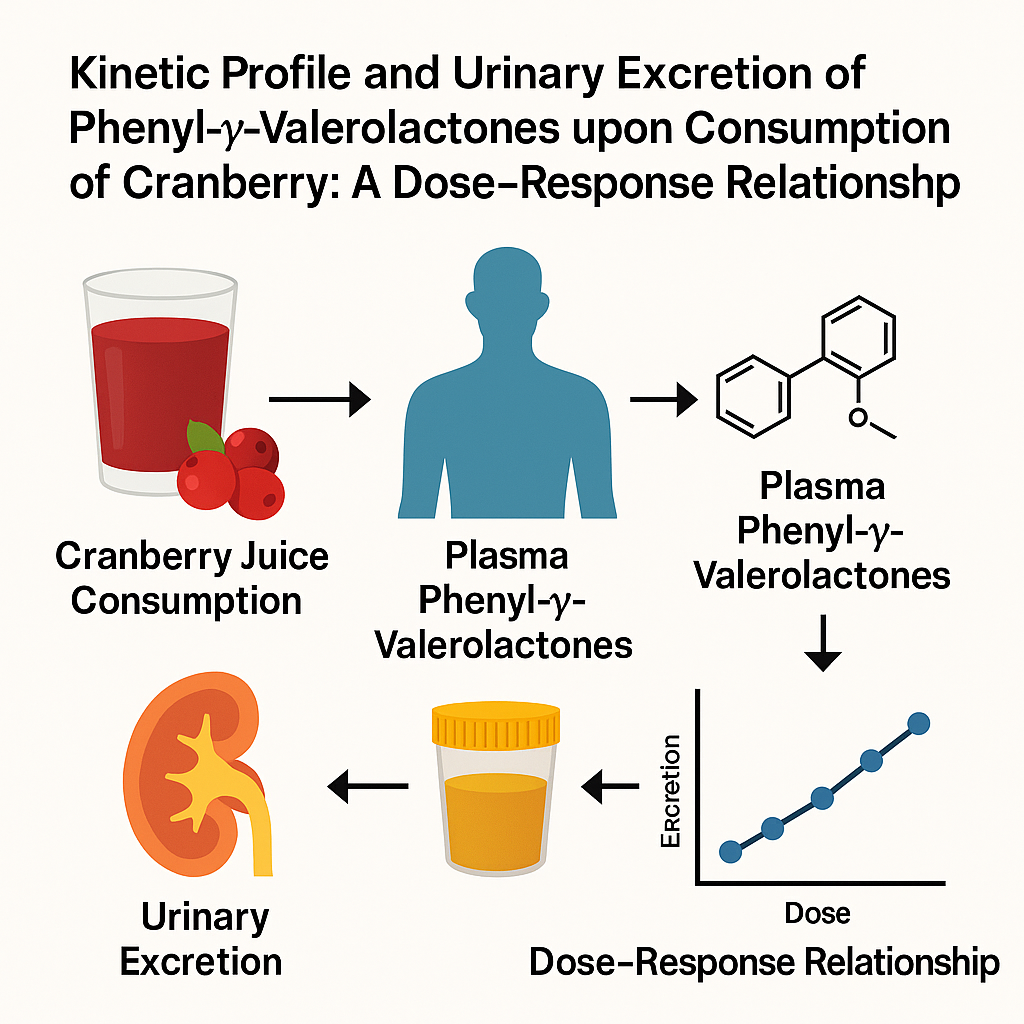
Favari et al. 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/D0FO00806K
This study found that cranberry polyphenols are broken down by gut microbes into smaller compounds, which were detected in blood and urine after consumption. Finding these metabolites in circulation shows that cranberry polyphenols are absorbed and become available to the body, though the amount varied between individuals depending on how efficiently their gut microbes carried out this process.
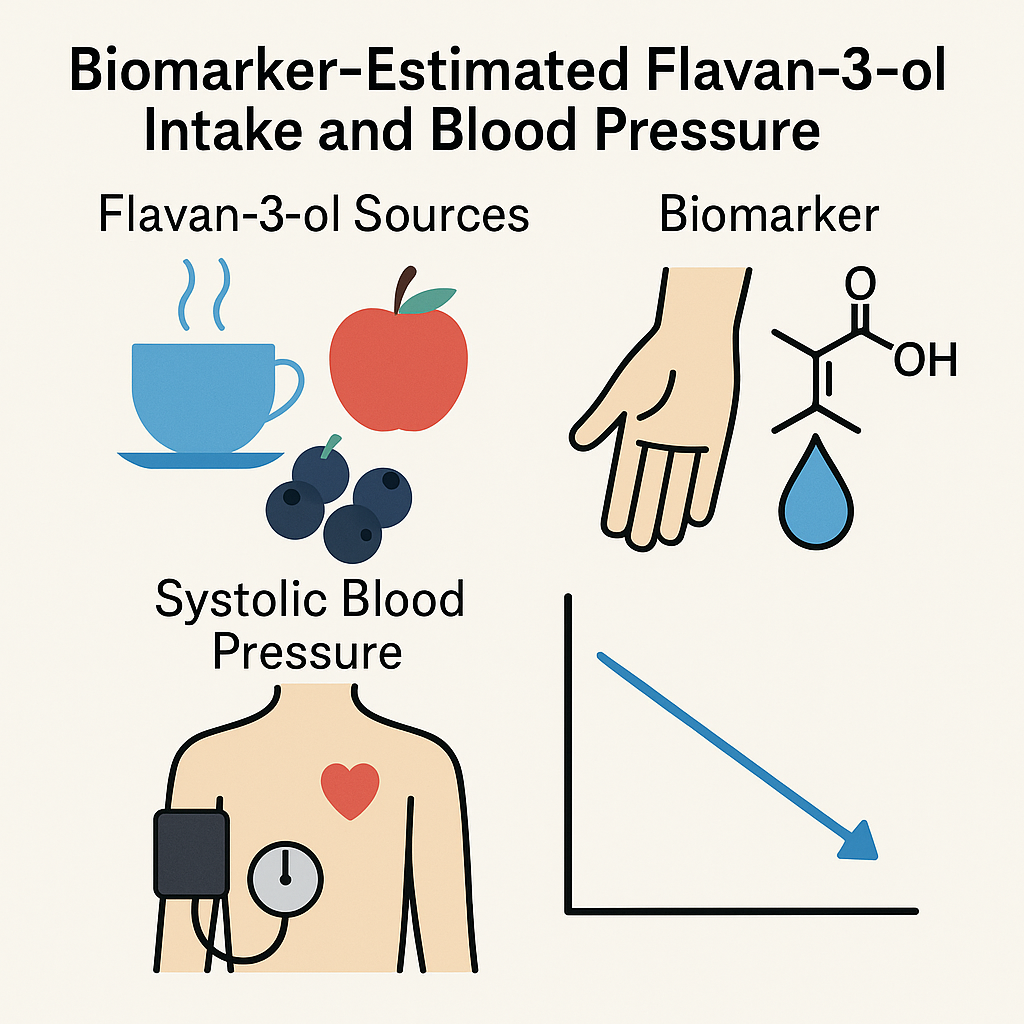
Ottaviani et al. 2020 | DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74863-7
This large observational study found that higher habitual intake of flavan-3-ols was associated with modestly lower blood pressure (about 2 mmHg lower systolic pressure in high vs. low intake groups). These small differences, while modest for individuals, could add up to meaningful benefits across a population.
Sansone et al. 2015 | PMID: 26348767
In a randomized, double-masked trial of healthy middle-aged adults, a cocoa-flavanol drink taken for four weeks improved a measure of blood-vessel function (flow-mediated dilation) versus control and modestly lowered blood pressure, arterial stiffness, and LDL/total cholesterol, leading to lower calculated 10-year cardiovascular risk scores.
Liu et al. 2022 | PMID: 35050355
In older adults, four months of urolithin A increased muscle endurance in hand and leg tests and reduced plasma biomarkers associated with mitochondrial function and inflammation; primary endpoints (6-minute walk distance and maximal ATP production) were not significantly different versus placebo.
Singh et al. 2022 | PMID: 35584623
In middle-aged adults, four months of urolithin A supplementation improved leg muscle strength and some performance measures, and favorably shifted biomarkers linked to mitochondrial efficiency and inflammation; the primary endpoint (peak power output) was not significantly different from placebo.
